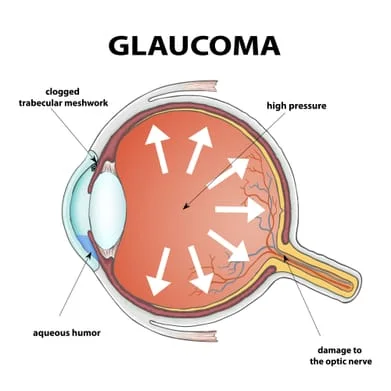
Glaucoma is a condition, typically without symptoms, that damages the optic nerve. Without treatment, it can lead to permanent, irreversible vision loss. It is often, but not always associated with increased pressure in the eye. Glaucoma is the second most common cause of blindness worldwide and the leading cause of blindness among African Americans. While the disease can be managed effectively with medications and surgery, there is currently no cure for glaucoma.
Symptoms Glaucoma is referred to as the “silent thief of sight” because there are no initial symptoms. The only way to diagnose the condition in its early stages is with an eye examination. Once lost, the damaged vision cannot be restored. Early detection and treatment is imperative in preventing vision loss.
Risk Factors Increased intraocular pressure is a main risk factor for glaucoma. Other risk factors include a family history of glaucoma, African/Latin descent, myopia (nearsightedness), diabetes, age, and certain medications.
Treatment Eye drops that lower the intraocular pressure are the mainstay of treatment. The goal of therapy is to prevent optic nerve damage and to preserve the visual field. There are several different classes of medication with different medications in each class. Both laser and intraocular surgery are reserved for more advanced cases or those that do not response to traditional medical therapy.